Introduction
In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly evolving, its potential to replace human roles in various fields is a hotly debated topic. The domain of UX research and design is no exception. To grasp the impact of AI in the field and examine the potential risks of AI replacing our UX jobs, we will align our reflections with the stages of the Human-Centered Design (HCD) process.
In our exploration, we’ll steer away from the versatile and well-known Chat GPT. Instead, let’s venture into less charted waters, examining a range of both acclaimed and critiqued AI-powered tools that are shaping, or perhaps disrupting, the landscape of UX.
1. Project definition & scope: Understanding business problems
AI’s role: AI can assist in defining the scope of a UX project by analyzing market trends, competitor strategies, and technological advancements. It provides valuable data-driven insights that can help shape the project’s direction.
Human expertise: Although AI offers data, the human element is crucial in interpreting this data in the context of real-world business problems. The ability to understand the nuances of market dynamics and align them with business goals is a distinctly human skill.
Assistive AI tools worth exploring:
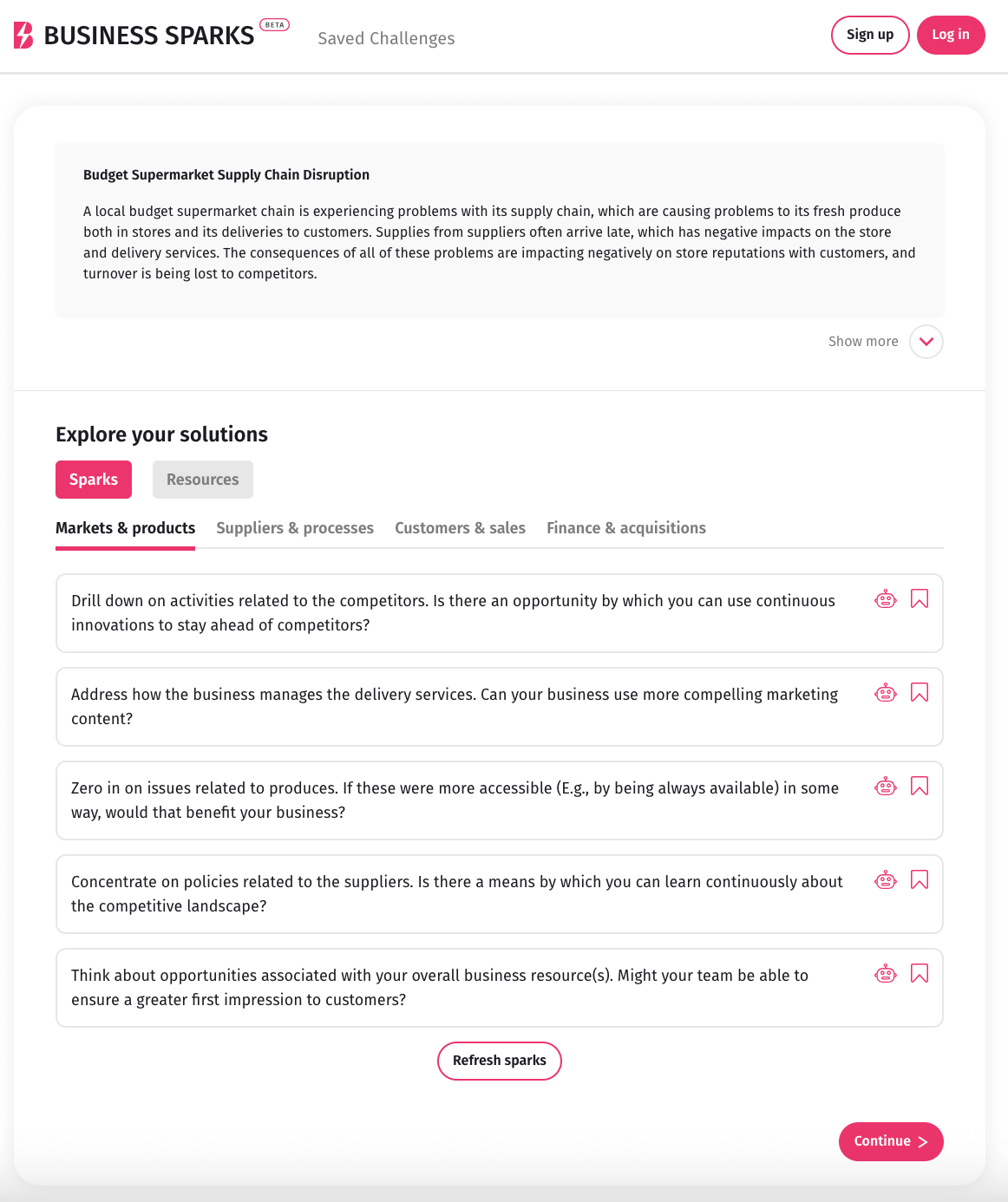
Business Sparks: An AI-enabled tool that helps to generate ‘business sparks’ within four categories: markets and products, supplies and processes, customers and sales, and finance and acquisitions. It’s designed to explore your business challenge, reframe it if necessary, and discover case studies and research papers related to your challenge.
AI Competitor Analysis Report Generator by Taskade provides insights into your rivals’ strategies, uncovering their strengths and weaknesses in seconds.
2. UX research: Understanding user problems and needs
AI’s contribution: AI tools can streamline the process of gathering and analysing user data. For instance, AI can efficiently analyse large volumes of user data to uncover patterns and preferences. However, AI tools might provide vague summaries and recommendations, and often lack context awareness and an understanding of human behaviours.
Human vital role: It is the task of the UX researchers to review the data (which might indeed be drafted by AI tools) and build personas and empathy maps, tasks where human intuition and emotional intelligence are irreplaceable. Currently, only humans can feel empathy and bring in an understanding of the context and intricate nuances of human nature and behaviours.
Support Tools for Your Research Sessions:
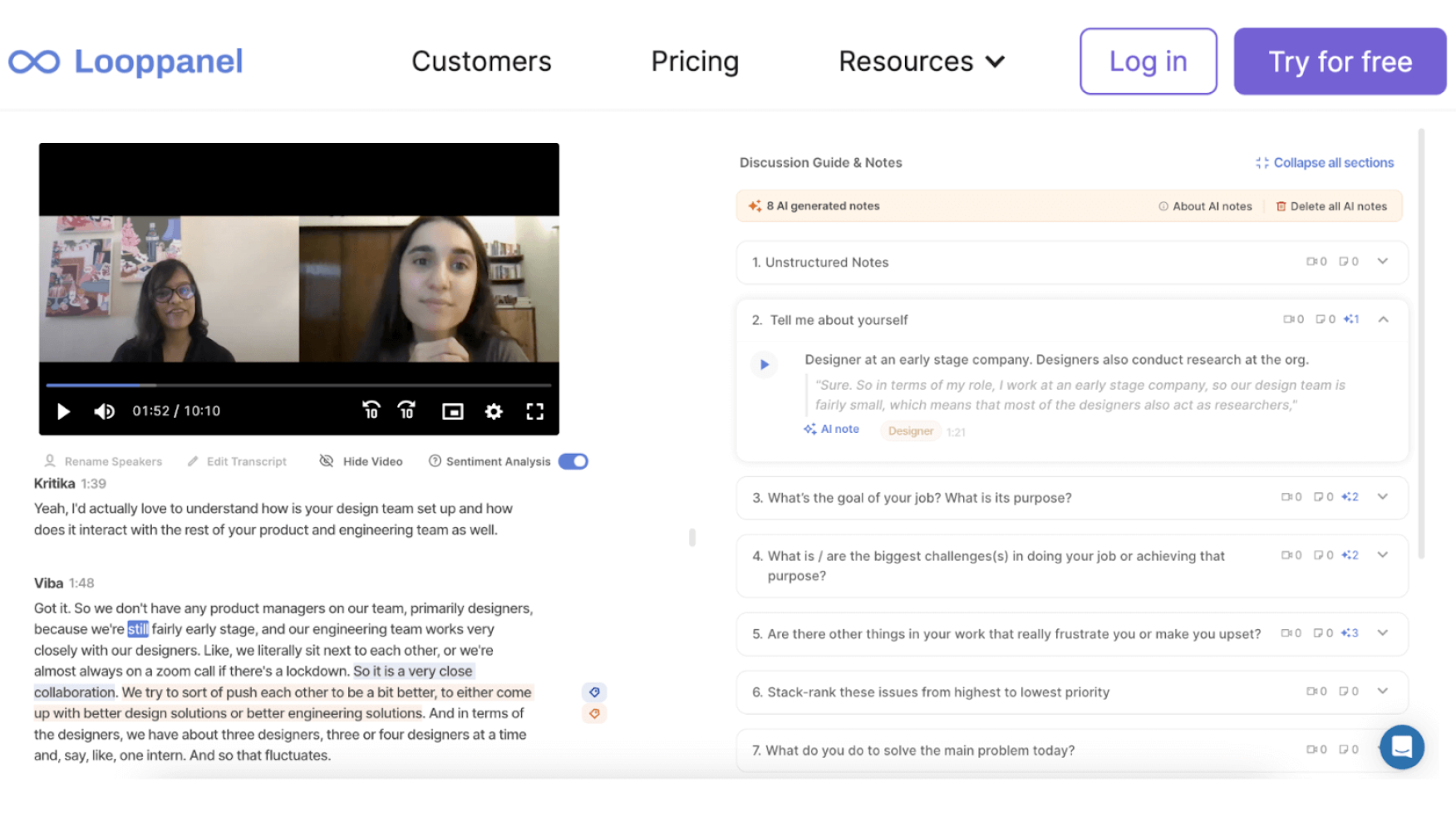
Particularly useful when dealing with transcripts and video, LoopPanel and Grain are similar handy tools that offer high-quality transcription services. They both feature time-stamped notes and the option to create video clips from specific transcript selections instantly.
Big data analysis tools: Kraftful & Viable: are comparable tools designed for analyzing large customer data from a variety of sources, such as user reviews, call transcripts, survey data, emails, feedback forms, and more, to generate actionable insights.
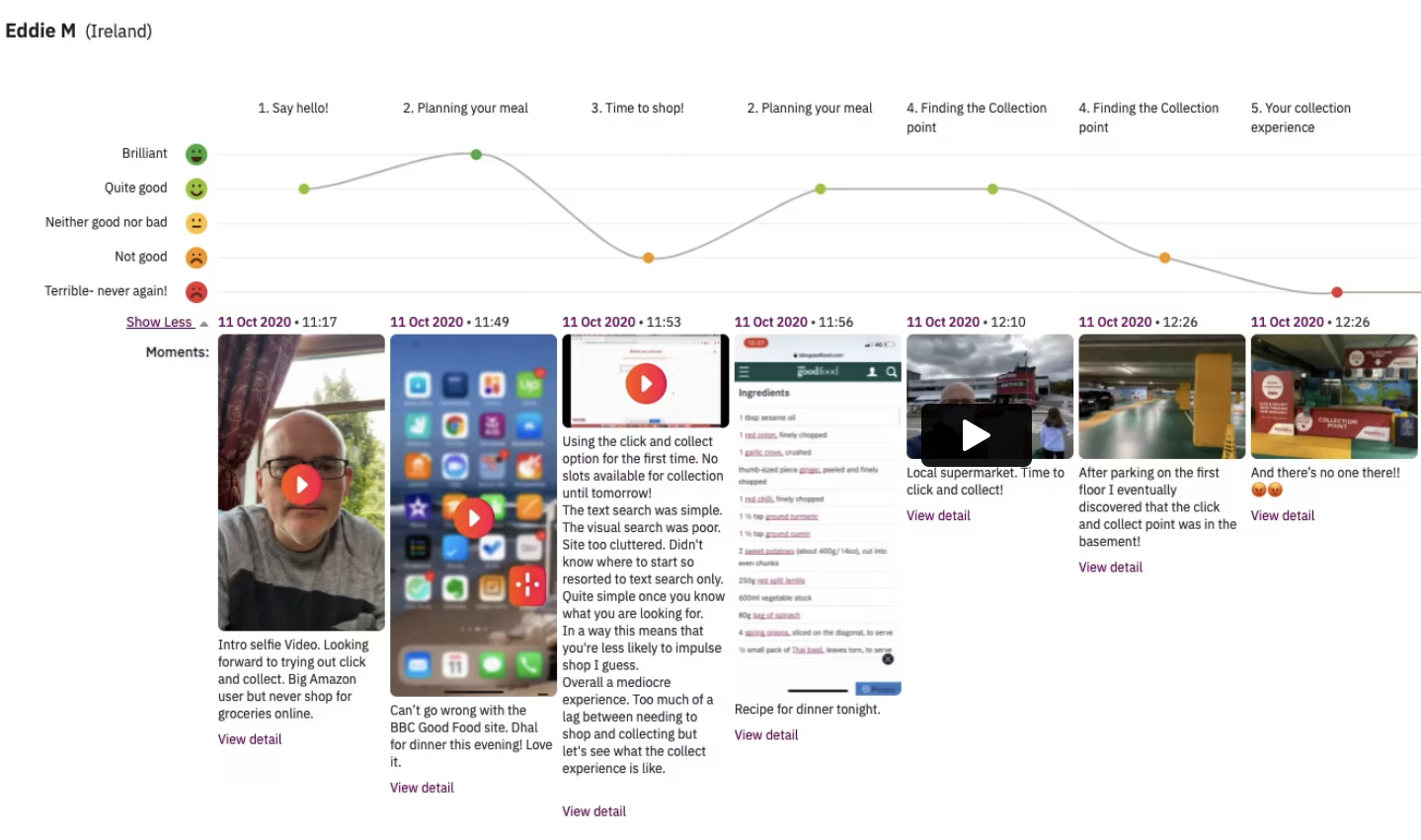
Indeemo: a great research tool which was enhanced with AI capabilities in 2023, making it especially valuable for large-scale qualitative studies involving mixed media, such as diary studies.
This tool is adept at capturing behaviours and experiences in real time using videos, photos, screen recordings, or text. It organizes data into a Pinterest-style dashboard and research repository.
Additionally, it analyzes and translates research content across 21 languages and automatically generates multimedia journey maps and user group experience graphs.
Symanto: A social monitoring tool that tracks discussions and mentions of your brand or product across social networks, forums, blogs, and other online platforms.

Debatable AI-moderated user research tool Outset.ai claims to be like ‘unmoderated user research on steroids’. You can customize the AI interviewer by selecting a persona, adding your discussion guide, and providing specific instructions. The tool can then conduct up to 1,000 interviews simultaneously in any language, synthesizing and summarizing the results, making it highly efficient for large-scale user research.
And one step further, the highly controversial tool Synthetic Users offers user research without humans but with synthetic users powered by AI. However, as discussed in this post, it fails to capture the essence of real people’s lives, relying on stereotypical data available online.
3. Ideation
AI’s functionality: AI can generate numerous potential solutions by rapidly iterating over design possibilities based on predefined parameters. This can inspire new directions and solutions that might not be immediately apparent to human designers.
Human creativity: Human designers play a crucial role in assessing the feasibility, desirability, and viability of these AI-generated ideas, making critical decisions that AI cannot.
Tools to support creative thinking
Design Sparks applies well-established creative problem-solving techniques, adapted for design projects, to help you discover your best solutions.
Dice.design claims to accelerate the design process by creating and sourcing design inspiration in seconds. It draws from some of the best user experiences in the world, though the specifics of these references are unclear.
4. Design and prototyping
AI’s efficiency: AI has the capability to automate certain tasks in design and prototyping, such as creating wireframes or basic prototypes based on patterns in user data. This automation significantly speeds up the design process, allowing designers to concentrate on more intricate and complex aspects of their projects.
Human ingenuity: The role of human designers is crucial in adding a personal touch, understanding the subtleties of user experience, and making design decisions that emotionally connect with users. Their creativity and insight are irreplaceable in crafting designs that truly resonate.
Highly praised tool in UI/UX circles Adobe Firefly features an AI tool that allows users to add, extend, and remove content from images using simple text prompts, fine-tuning the results to perfection within Photoshop.
A tool worth exploring for entry-level designers or companies without a design system is Uizard. It enables the quick creation of visually appealing designs. The tool can convert screenshots into editable mockups or generate new ones from a brief description. Additionally, it allows users to add clickable user journeys to their UX prototypes, enhancing interactivity and usability.

5. Testing
AI’s precision: AI can offer precise quantitative analysis in testing. It can simulate user interactions and predict the impact of changes on user behaviour. However, completely replacing human involvement in this phase is a formidable challenge. AI currently lacks the nuanced skills required for direct human interaction and is not yet adept at detailed observational tasks.
Human insight: Conducting user testing that involves observing behaviour, as opposed to merely registering what people say, remains an irreplaceable task for human researchers. Analysis based solely on transcripts can miss the crucial context. Understanding and incorporating the subtleties of context and users’ past experiences require human involvement. The ability to empathize with users and adapt based on subtle feedback is a skill unique to humans.
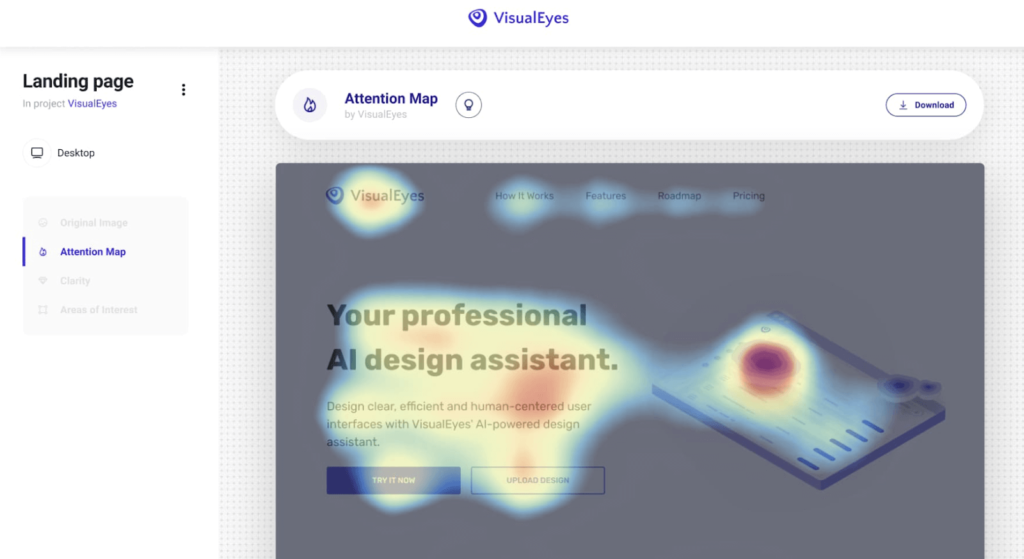
This AI tool VisualEyes helps simulate eye-tracking tests to predict where users’ attention might focus. It offers in-depth insights within seconds based on extensive data from large-scale studies and boasts a 93% accuracy rate.
Conclusion
Our journey through the Human-Centered Design process highlights that AI is not a replacement for UX professionals’ work. It does bring efficiency and speed, but the human element is crucial.
The future of UX research and design rests on a collaborative synergy between AI and human expertise, each enhancing the other.
In this context, AI can be likened to a Junior UX Consultant, offering unique strengths:
- Endless energy and willingness to perform mundane tasks.
- Fresh perspectives and diverse viewpoints.
It also has specific requirements:
- Initial onboarding: AI needs initial training and programming, similar to a new team member, to understand specific project requirements and adhere to company standards.
- Ongoing monitoring: Regular oversight is essential to ensure that AI tools stay aligned with project goals and function correctly.
For experienced UX professionals, AI is not a threat but a valuable tool that streamlines and improves their workflow. For newcomers, it means learning to work with AI from the start, adding a new dimension to their professional development.
Need support with your UX research and design?
Bunnyfoot has always prioritised evidence capture and valid, bespoke study designs to truly understand the nature of user engagement, interactions and behaviours, in a holistic way.
If you would like to talk about how we can support you with gaining a deeper understanding of your audience so you can make evidence-driven design decisions, we’d love to talk! Contact us.